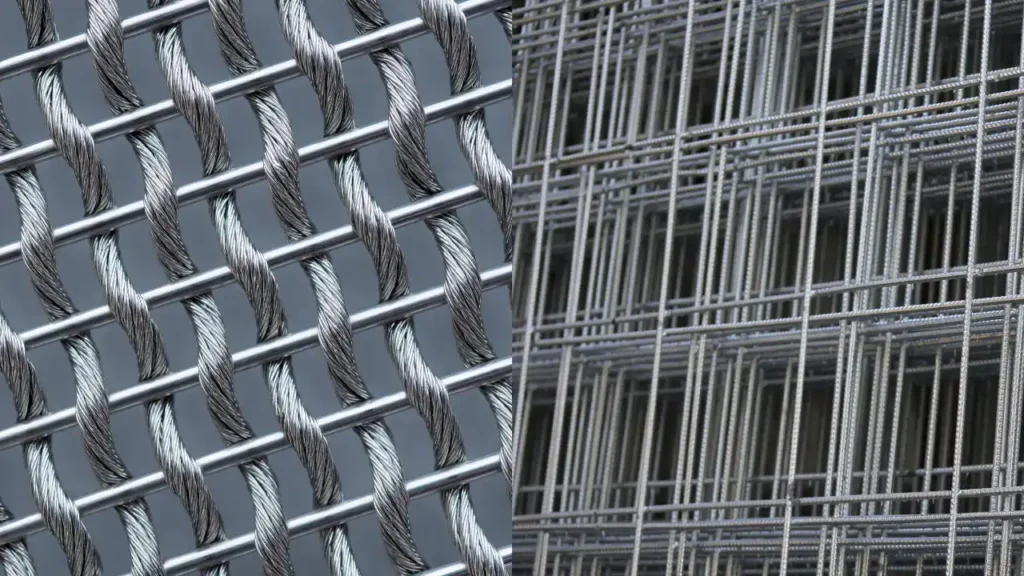
There are several industries where Wire Meshes are used on a routine basis – FMCG, Pharmaceuticals, Oil and Gas, Construction to name a few. Among a dozen different solutions available Welded and Woven Wire Mesh are the most widely used.
But then which works best – Woven or Welded?
To determine this, one needs to address several important prerequisites – application of the mesh, materials of mesh being used, stage of work where mesh will be used.
Al Miqat Hardware has been providing quality Wire Mesh Solutions for over 15 years now and has depth knowledge and understanding of the requirements of this MENA region.
In this blog, we shall discuss the difference between welded and woven wire mesh, the production of each type, the application for both techniques, and the costs involved. At the end of this article, you can decide which type works best for your requirements.
Woven Wire Mesh | Production
When this type of mesh is woven, a predefined amount of wires are wrapped around a warp beam that gets positioned into a special weaving loom. The warp wires are then placed into frames that split the wire into 2 or more sets based on the pattern of wire mesh.
As the loom operates, the frames push the different sets of wires up and down as a wire, known as the shute wire, is driven in between the wires. After being threaded through the wires, the up and down motion of the heddle frames locks the shute wire into place.
Woven Wire Mesh | Application
The Mesh opening is finer in woven wire mesh. This is because as the wire diameter gets smaller, the harder it is to weld the mesh without damaging the wires or compromising the openings of the mesh. Hence this type of mesh is preferred for applications such as filtration and particle analysis.
This technique of wire mesh production involves welding steel wire at wire cross-sections using several techniques, the most common being Spot Welding. As the wires undergo the welding process, the opening size of the mesh is for the most part permanent.
Welded Wire Mesh | Production
During the production of this type of mesh, spools of wires are threaded into a welded mesh machine, much like threading wires into the heddle frames and reed of a woven wire loom. Separate spools of wire are then fed through a straightener and pre-cut to match the desired width of the mesh.
As the machine runs, the wires from the spools are fed through the machine. The pre-cut wires are then placed into a mechanism that lays them across the wires being fed from the spools.
After being laid in place, the machine applies a uniform weld at each cross-section simultaneously. Depending on the length of the welded wire mesh fabric, the mesh is either rolled by the machine or operators take the mesh, cut the access material, and place it into a pile.
Welded Wire Mesh | Application
The nature of this type of wire mesh requires the use of thicker wires to withstand the welding process. Hence Welded Wire Mesh is more rigid and durable as compared to Woven Wire Mesh. The strength provided by this type of wire mesh makes it an ideal choice for road works, perimeter fencing, reinforcement, and animal cage in zoos.
Woven vs Welded Wire Mesh | Cost Analysis
As discussed previously, welded mesh and woven wire mesh are produced differently. The Woven Mesh production process is mostly automated.
Welded Mesh, on the other hand, is a lot more hands-on. An operator must thread a wire through a straightener before it is cut into the crossbars. The additional wire must also be threaded through the machinery itself. Lastly, the access material that protrudes off the edges must ensure optimal results. Again this process is commonly done manually when the mesh is not being rolled by the machine.
Considering this, the labor costs and heavy-duty wire that must be used cause welded mesh to be the more costly of the two.
Woven vs Welded Wire Mesh | Which is better?
Just like all other wire mesh, the application will determine which is better – Woven or Welded Wire Mesh. If the application requires working with rugged material then wire mesh that is durable and sturdy may be a good fit. Welded Mesh is also advisable for extremely corrosive conditions where galvanizing can be applied for extra protection. Woven Wire Mesh on the other hand can be considered where strength is not required and the aperture size is lower than ¼” (6mm). This solution is also cost-effective as compared to the other technique. Generally, Woven Wire Mesh is also produced with stainless steel, hence it is resistant to corrosive material. Also, this technique has a shorter lead time in production.
All said and considered, Woven Wire Mesh may be a better choice.
For more information visit our website Al Miqat Hardware.